

The second number indicates the regional area in the state, the third number is for the routing allocation, following railways and post car routes and the fourth number indicates the post office. 6xxx: Tyrol and Vorarlberg (without East Tyrol).Postal codes in particular countries AlgeriaĪustrian post codes were introduced in 1966 and consist of four numbers. In New Zealand, Auckland, Wellington and Christchurch were divided into postal zones, but these fell into disuse, and have now become redundant as a result of a new postcode system being introduced. Ireland still uses postal district numbers in Dublin.
#Postal 4 digit code code#
The newer postal code systems often incorporate the old zone numbers, as with London postal district numbers, for example. The independent nations using alphanumeric postal code systems are:īefore postal codes as described here were used, large cities were often divided into postal zones or postal districts, usually numbered from 1 upwards within each city. Alphanumeric systems are often more accurate, as in the case of the United Kingdom or the Netherlands, where a postal code in its original form corresponds right down to a street or even a building, meaning the post code and the number of the home/business is all that is needed for accurate delivery. Many postal code systems are numeric, but some are alphanumeric (i.e.
#Postal 4 digit code iso#
The European Committee for Standardization recommends use of ISO Alpha-2 codes for international postcodes and a UPU guide on international addressing states that "administrations may recommend" the use of ISO Alpha-2 codes. Usage of ISO 3166-1 alpha-2 codes was recommended to be used starting in 1994, but did not become widely used. For many years, licence plate codes - for instance "D-" for Germany or "F-" for France - were used, although this was not accepted by the Universal Postal Union (UPU). Recommendations by official bodies responsible for postal communications are confusing regarding this practice. In some countries (such as those of continental Europe, where a postcode format of four or five numeric digits is commonly used) the numeric postal code is sometimes prefixed with a country code to avoid confusion when sending international mail to or from that country. In most English-speaking countries, the postal code forms the last item of the address, whereas in most continental European countries it precedes the name of the city or town. Postal services have their own formats and placement rules for postal codes. No Chinese postal codes are assigned to Hong Kong.Īlthough postal codes are usually assigned to geographical areas, special codes are sometimes assigned to individual addresses or to institutions that receive large volumes of mail, such as government agencies and large commercial companies. Another example is Hong Kong = although Hong Kong has become a special territory of China in 1997, Hong Kong maintains its own long-established postal system and does not use any postal code for domestic mails within Hong Kong. Examples of countries that do not have national systems include Ireland and Panama. In February 2005, 117 of the 190 member countries of the Universal Postal Union had postal code systems. The United Kingdom followed in 1959 and the United States in 1963. Germany was the first country to introduce a postal code system, in 1941.
#Postal 4 digit code series#
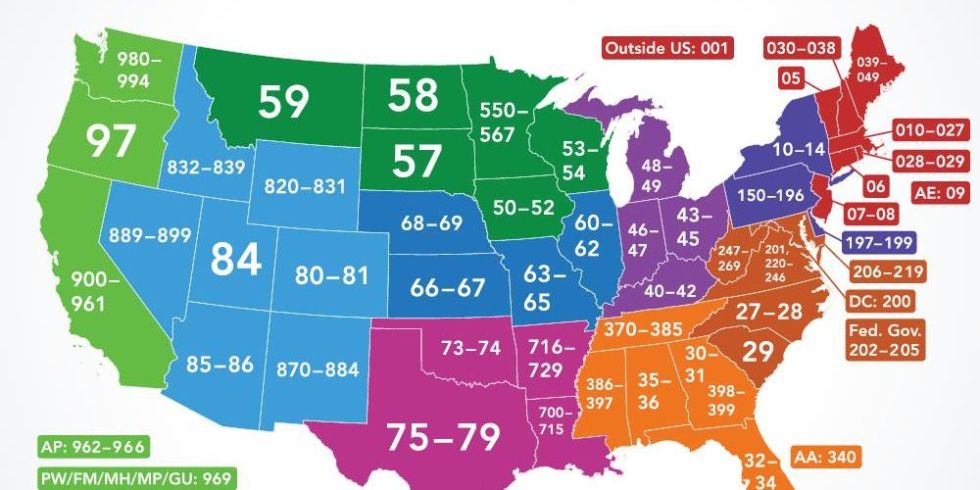
Many countries provide the public with books in which a postcode can be looked up.Ī postal code (known in various countries as a post code, postcode, or ZIP code) is a series of letters and/or digits appended to a postal address for the purpose of sorting mail.
A Dutch postcode book, dating from when postcodes were introduced to The Netherlands in 1978.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
